2025-04-03
There are about 100 billion neurons in the human brain. Any seemingly simple thing in an individual involves a large number of neurons involved in it. Of course, these neurons are highly orderly in activities, and the local field potential (LFP) in the brain that allows many neurons to move together is like a "trumpet" that directs neurons to work. Gamma oscillation is a relatively important type of local field potential in the brain, which is about 25-70 (average 40) Hz oscillation. Gamma oscillation was the earliest phenomenon reported by Wolf Singer, the Maxford Brain Institute in France in the 1980s.
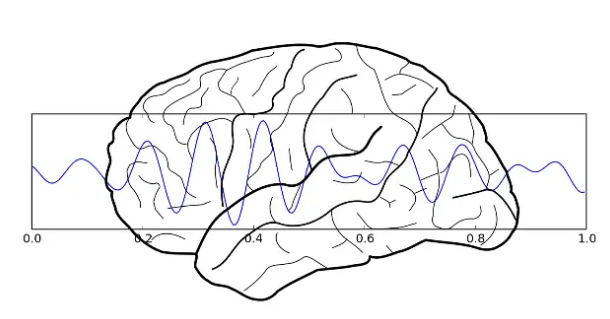
After discovering the DNA structure, Crick shifted his direction to the neurobiological basis of human consciousness. This gamma resonance signal is a phenomenon that Crick has always hoped to look for. He believes that consciousness is like music produced by neuronal resonance, it is an uninterrupted connection resonance across different brain regions, but consciousness is music, changing the melody at all times.

Neurons form field potentials, which should be the resonance formed by a large number of neurons. Neuron excitation has a specific frequency, which is a common feature of all cell potentials, because the excitatory cell produces an action potential that will cause cell membrane discharge. After the discharge is over, a charging process is required. This charging process is called a refractory period, which means that no excitation will be performed in a short period of time after excitation. The basis for these characteristics is the electrophysiological phenomenon of the cell mainly composed of sodium ions and potassium ion channels on the cell membrane. Among them, sodium-potassium ATPase is responsible for establishing an ion gradient, increasing potassium ions in the cell and reducing sodium ions. These form an ion concentration gradient inside and outside the cell. This gradient forms a cell voltage. The development of sodium ion channels establishes a certain resting potential. The opening of potassium ion channels is similar to battery discharge, forming a transient pulse current. This electrophysiological characteristic determines the excitation of the cell membrane needs to be at a certain interval, and the overall manifestation is a certain frequency.
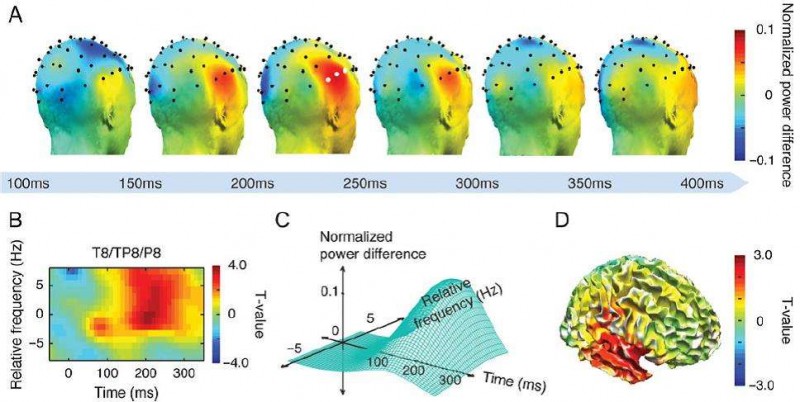
Neurobiology calls this phenomenon of resonance activation between neurons in common frequency called neural handshake. Although there are hundreds of billions of neurons in the brain, any two neurons can be connected through direct and indirect pathways. If there are similar frequencies between these connections, the basis for handshake and resonance is generated. Neurons with close frequencies can form electrical synchronization, which is similar to various physical phenomena that resonate at the same frequency. Gamma oscillation is actually a synchronous resonance phenomenon formed by nerve cells in different regions of the brain. This resonance may be the basis for the brain to produce advanced functions such as consciousness.
Important evidence that this gamma oscillation is closely related to advanced neurological function is that the degree of this oscillation signal loss in patients with senile Alzheimer's disease is closely related to the severity of the disease. Some scientists have also intervened in this phenomenon. The more famous one is the 2016 MIT research team, which was closely related to learning and memory, stimulated the interneurons of the dentate gyrus to induce gamma oscillation through optogenetic technology. It was found that the induced gamma oscillation can reduce the production of Aβ in the brain of mice with Alzheimer's disease model, improve the learning and memory ability of animals, and achieve the purpose of treating Alzheimer's disease in animals. Later, this stimulation was further simplified, and the use of retinal light flicker signal stimulation can also induce weakened gamma oscillation signals. In 2019, the same effect can be produced by using sound oscillating with similar frequencies in a more discontinuous way.
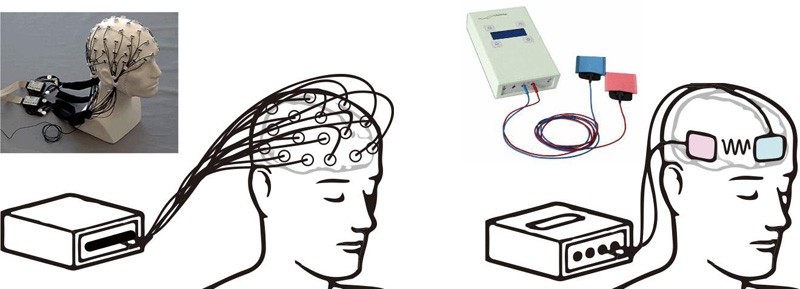
Imagine that there are two non-nounciation stimulation methods for stimulating the brain, one is transcranial direct current stimulation and the other is transcranial magnetic stimulation. The effects of this specific frequency may not be studied in the past. If these stimulations are improved, it may become a better stimulation tool to activate gamma oscillation. If such stimulation has the effect of treating Alzheimer's disease, it may be an embarrassing situation in which there is no medicine available for Alzheimer's disease in the medical field today. Transcranial magnetic stimulation was used in the 1990s and has been sold in commercial stimulation helmets. Professor Posinger, a professor at Laurenson University in Canada, once used this method to stimulate the temporal lobe, causing the subject to experience vision and feel the appearance of God or the devil, so this helmet is even called the God helmet. In 2003, the British documentary "Horizon" once invited Dawkins (the author of "The Selfish Gene") to try this helmet, but it failed.